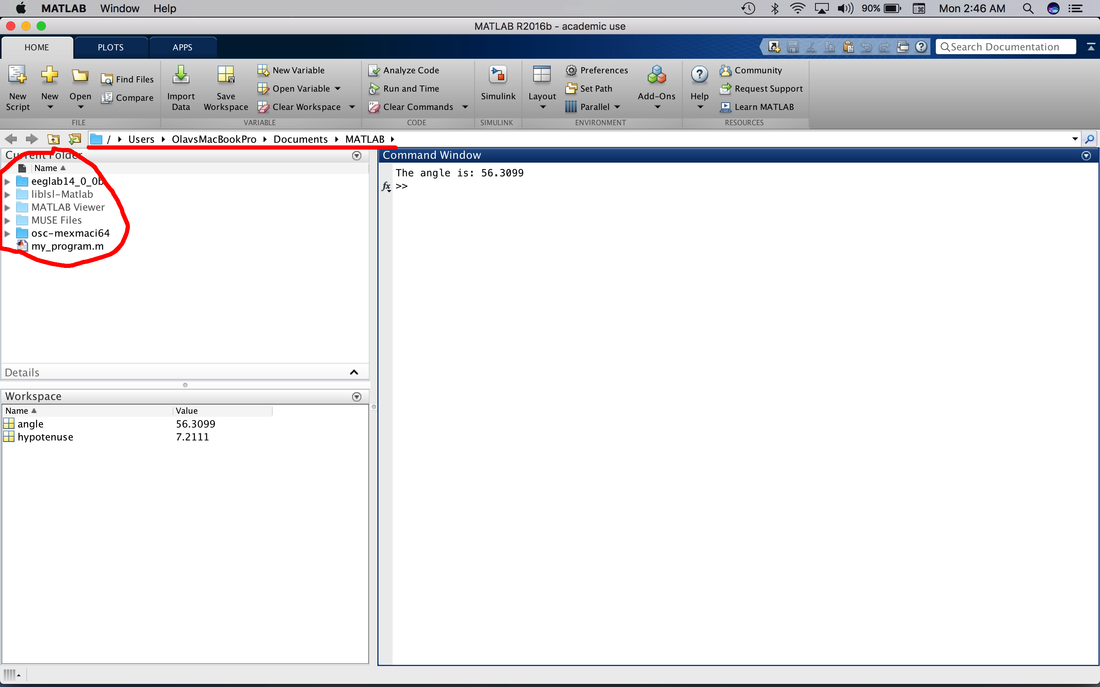
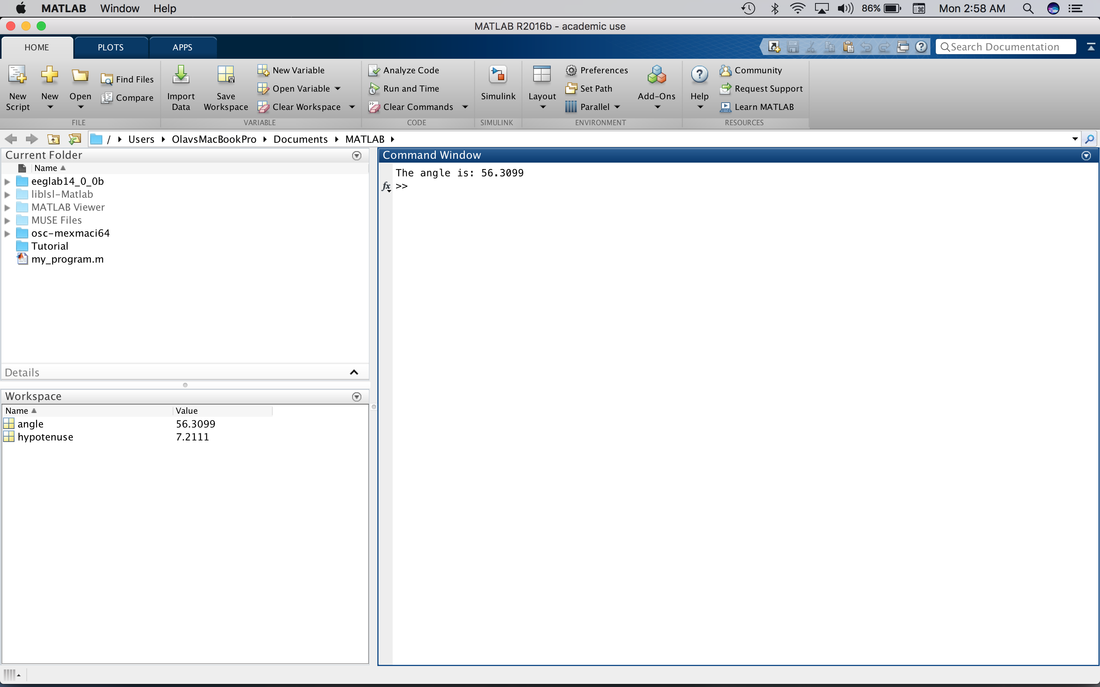
So, we have just written our first program. Where was it saved? If you look at the command window you will see the default MATLAB directory (underlined in red) and a list of the folders and files in the directory (circled in red).
MATLAB typically creates a folder (MATLAB) in your documents folder to store m-files and related directories. My directory already has some other folders in it. Note, Psychtoolbox does not install here automatically but you can put it here if you wish.
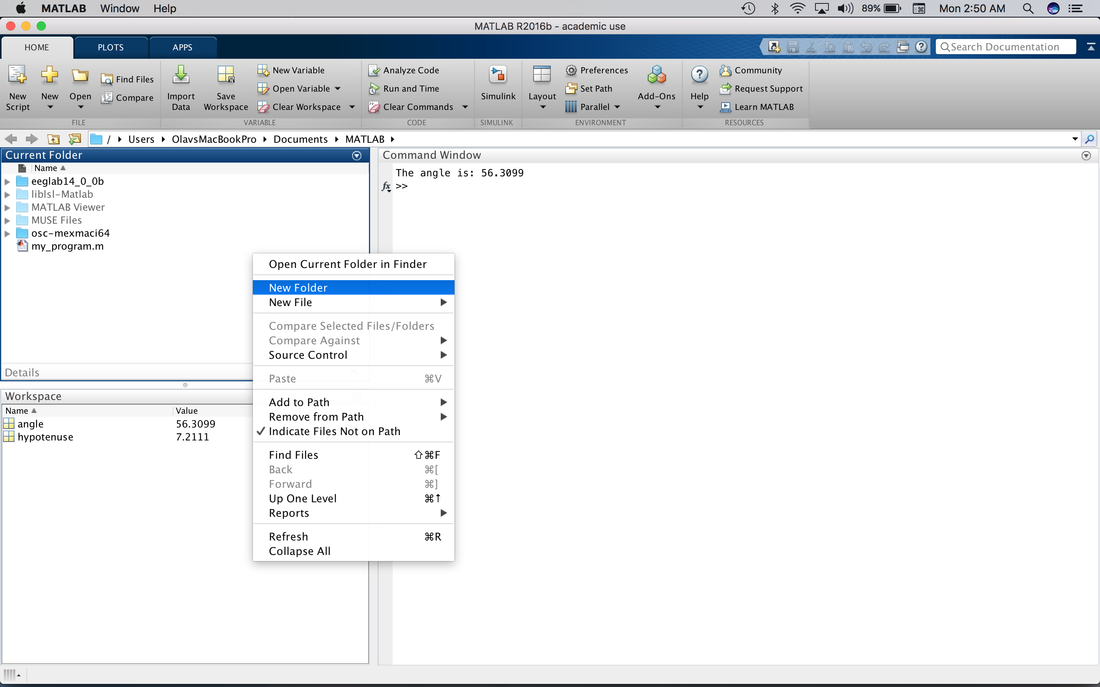
Let's create a folder for the programs we make in this tutorial. Right click in the Current Folder window and create a new folder called "Tutorial".
Let's create a folder for the programs we make in this tutorial. Right click in the Current Folder window and create a new folder called "Tutorial".
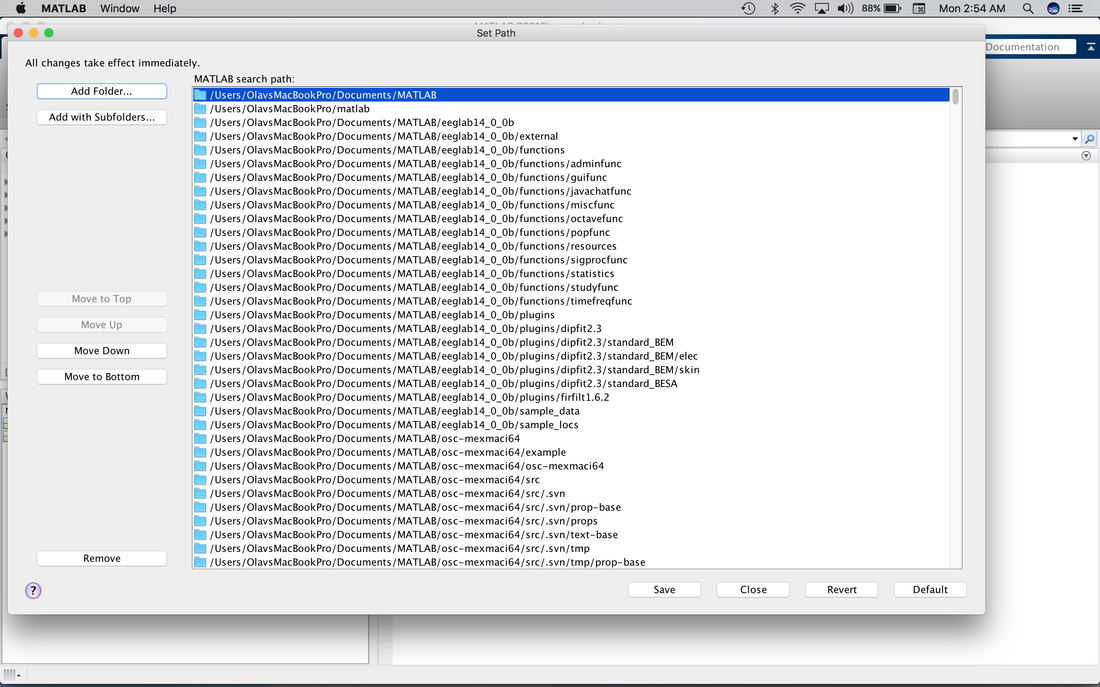
You will notice that the folder is washed out a bit. This is because it is not in the MATLAB path. What is the path? The path is where MATLAB looks for m-files. You have to physically add new folders to the MATLAB path. Otherwise MATLAB cannot "see" the m-files in them. Click on "Set Path". You should see the following screens.
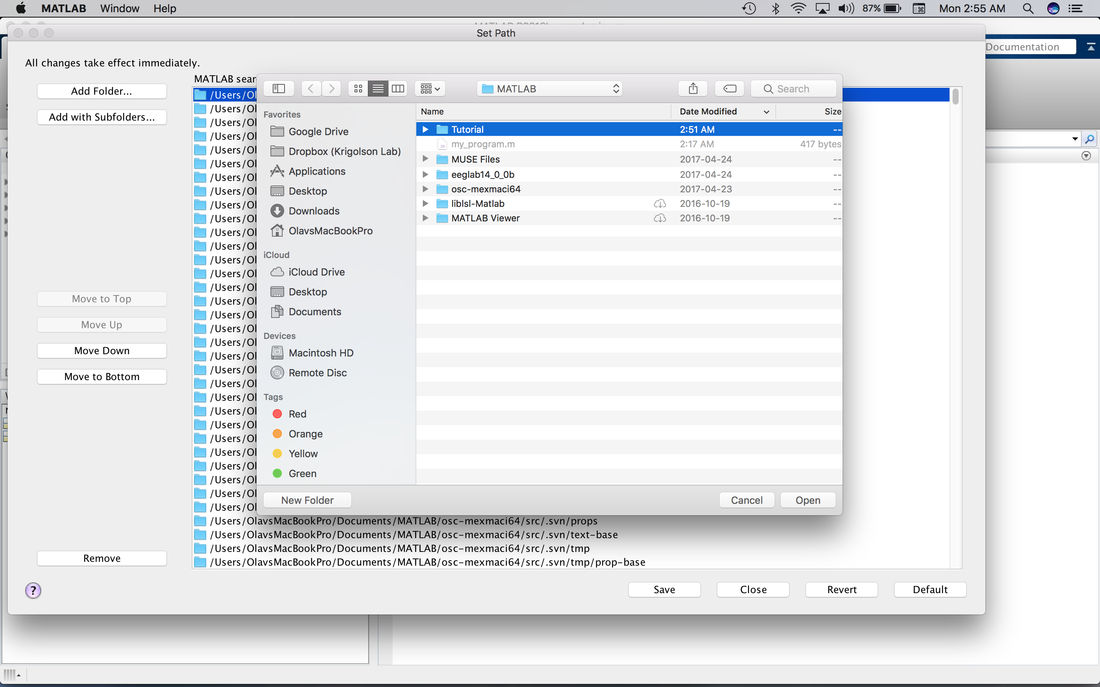
Click on Add Folder. Select Tutorial and click on Open.
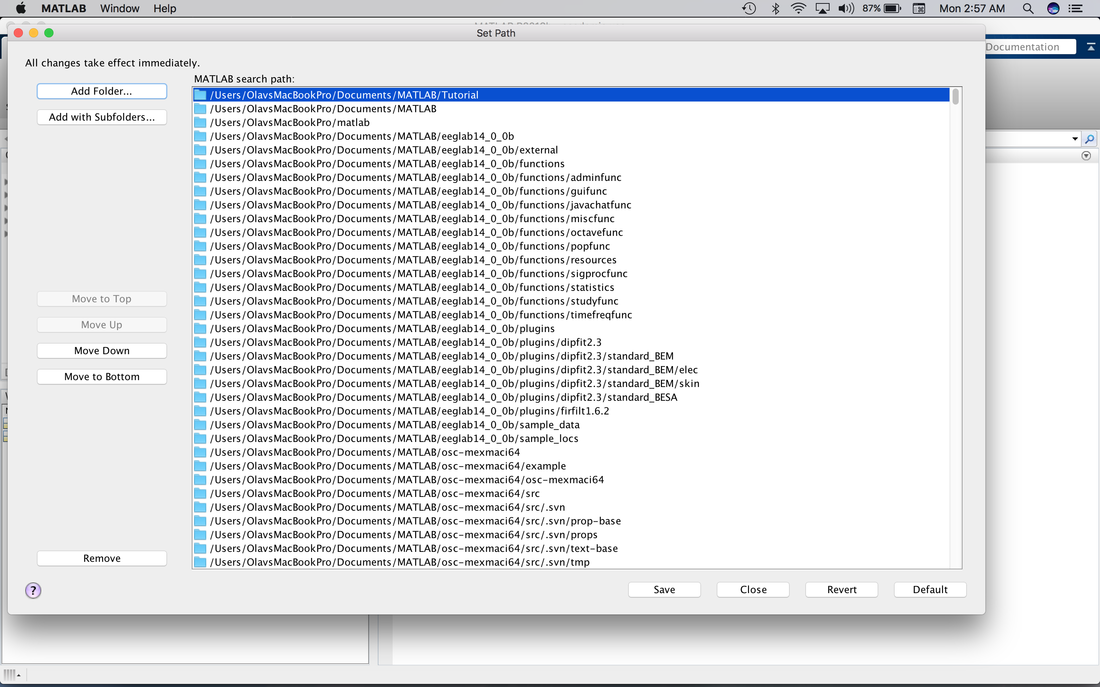
This will take you back to the previous screen, but you will see Tutorial at the top of the MATLAB path.
Click on Save then Close and you will have added Tutorial to the MATLAB path.
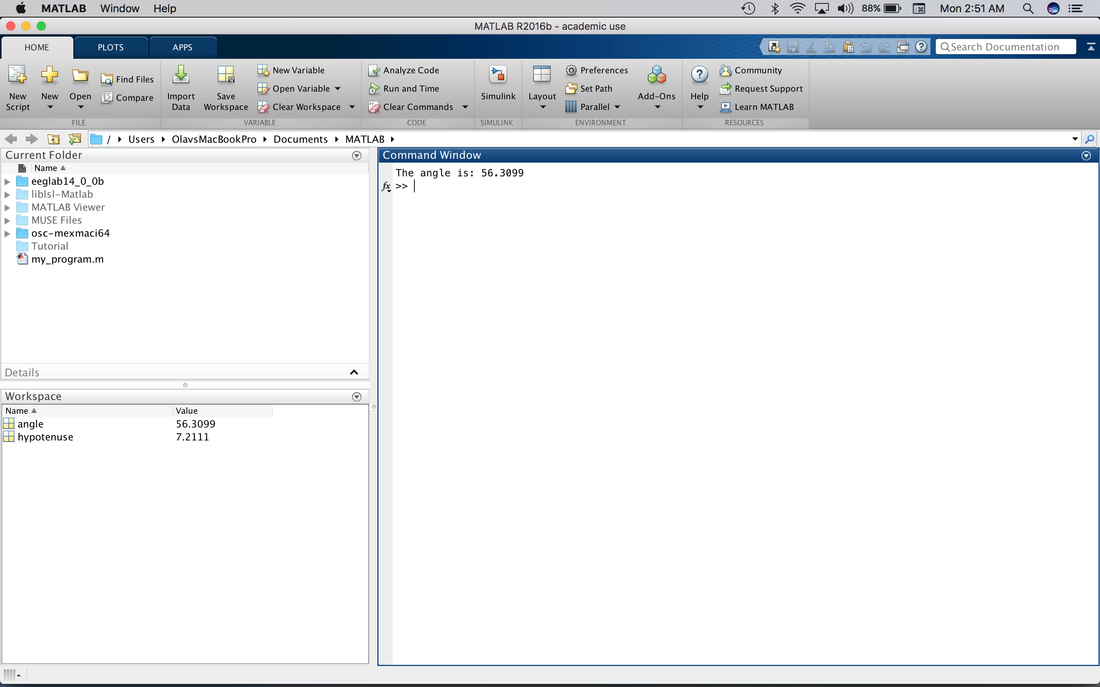
You will notice that Tutorial is no longer washed out but is in bold. This means it is in the path. Also, because we saved the path it will stay in the MATLAB path until you remove it. So, when you open MATLAB again you will not need to add it. Drag my_program.m into Tutorial. Double click on Tutorial. You will note that the Current Folder view is changed so all you see is my_program.m. You will also note that the Working Directory is changed. You can change the directory easily by using the cd command in the Command Window.
cd('~/Desktop')
This command would set the Desktop as the Working Directory. If you try this command out, make sure you set the Working Directory back to Tutorial after. Note, this is in OSX format. This differs slightly on a PC. I am sure you can figure it out by looking at the Working Directory bar.
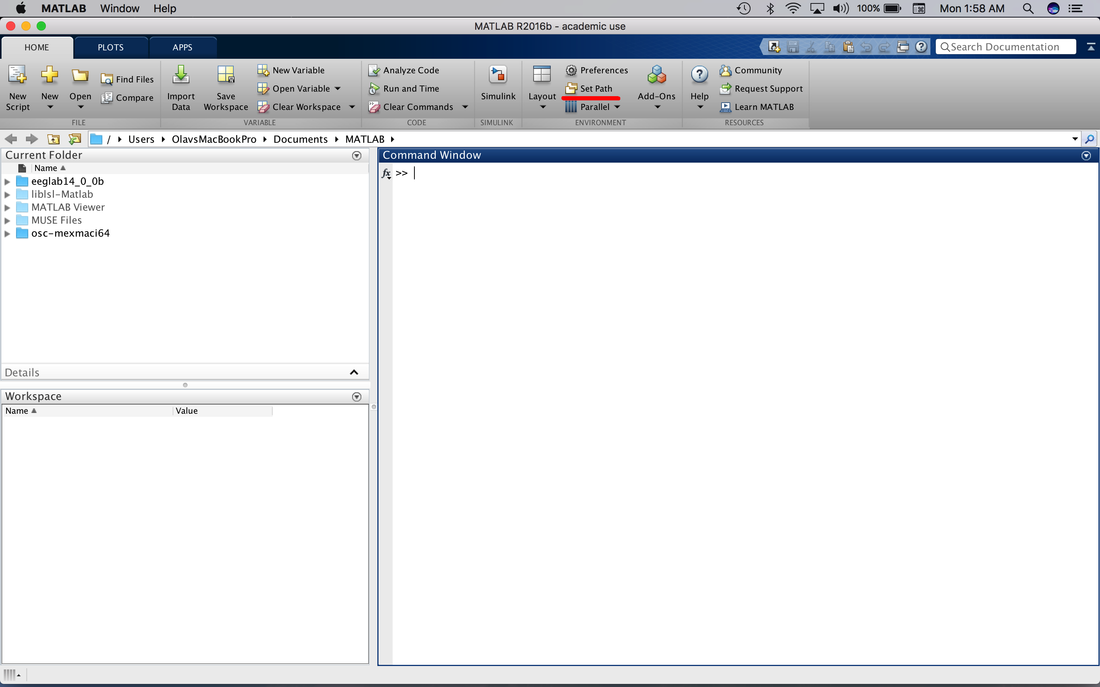
IMPORTANT. Paths in MATLAB can be dangerous! If you have multiple programs with the same name MATLAB will run the one in the current Working Directory or the first instance of the program it finds if it is not in the Working Directory. As such, try to ALWAYS use unique filenames or be very careful about what is in the path. Also, it is a good idea to use the help command to see if a filename is taken. If you clear all and then try help angle you will see that it actually is already a MATLAB function. To make my_program.m safe, lets make a few changes. Update your code to:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
the_angle = atand(6/4);
the_hypotenuse = 6/sind(the_angle);
disp(['The angle is: ' num2str(the_angle)]);
This will ensure that we are not using an existing MATLAB function as a variable name. Save or run this code and move onto the next tutorial!
cd('~/Desktop')
This command would set the Desktop as the Working Directory. If you try this command out, make sure you set the Working Directory back to Tutorial after. Note, this is in OSX format. This differs slightly on a PC. I am sure you can figure it out by looking at the Working Directory bar.
IMPORTANT. Paths in MATLAB can be dangerous! If you have multiple programs with the same name MATLAB will run the one in the current Working Directory or the first instance of the program it finds if it is not in the Working Directory. As such, try to ALWAYS use unique filenames or be very careful about what is in the path. Also, it is a good idea to use the help command to see if a filename is taken. If you clear all and then try help angle you will see that it actually is already a MATLAB function. To make my_program.m safe, lets make a few changes. Update your code to:
clc;
clear all;
close all;
the_angle = atand(6/4);
the_hypotenuse = 6/sind(the_angle);
disp(['The angle is: ' num2str(the_angle)]);
This will ensure that we are not using an existing MATLAB function as a variable name. Save or run this code and move onto the next tutorial!